Feeling Off-Balance? Try These Exercises
As you age, staying steady on your feet can become more difficult. Over one in four people aged 65 and older falls every year,...
Posted on August 16, 2022
EarAccording to the National Library of Medicine, the Eustachian tubes are narrow passageways that connect the middle ear to the back of the throat. They typically remain closed but open when you chew, swallow or yawn. The Eustachian tubes have three main functions: protecting the middle ear from pathogens, ventilating the middle ear to equalize air pressure with the environment and draining fluids from the middle ear.
Sometimes, the Eustachian tubes can malfunction. This is known as Eustachian tube dysfunction. We cover everything you need to know about Eustachian tube dysfunction below.
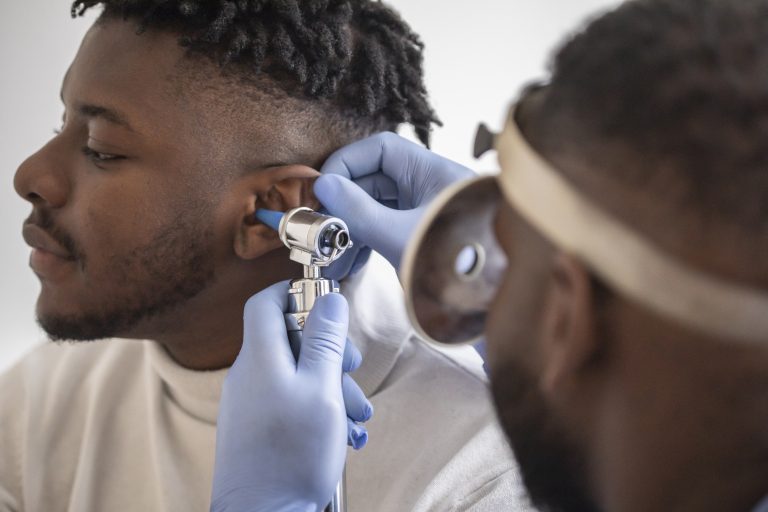
There are three main types of Eustachian tube dysfunction:
Common symptoms of Eustachian tube dysfunction include:
The most common causes of Eustachian tube dysfunction include allergies and infections like the cold and flu. Conditions like these cause inflammation and mucus buildup, including within the Eustachian tubes. Altitude changes, like when taking off or landing at Philadelphia International Airport can also cause Eustachian tube dysfunction.
In most cases, Eustachian tube dysfunction clears up on its own. It can also be managed with:
For more information or to schedule an appointment, call today.
As you age, staying steady on your feet can become more difficult. Over one in four people aged 65 and older falls every year,...
Tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, affects quite a few Americans daily—about 15% of them, according to results from the recently released Apple Hearing...
Sleep is essential to your health and well-being, yet many people struggle to get their full eight hours. One often overlooked obstacle to a...
Summer is the perfect time to enjoy endless days of swimming. Wherever you choose to soak up the sun and enjoy the water, it’s...